Abstract
Selecting the optimal location for a new bank branch is challenging but worth studying due to its importance to the success of the business.
In recent years, the proliferation of multisource data in smart cities has promoted the development of the data-driven methods on this issue.
Previous studies have been devoting lots of effort; however, they usually focus on mining different features and process these data through domain expert knowledge.
Therefore, they fail to discover potential complicated factors interactions. Besides, most of these studies only use a single indicator to evaluate the candidate locations, which overlooks a lot of information, resulting in an inaccurate evaluation.
In this study, we propose MATE, a Multi-task Attentive Tree-Enhanced model. With the financial embedding module and attentive interaction block, MATE learns the interactions of cross features and can simultaneously predict multiple performance indicators of a bank branch’s location.
In addition, MATE takes advantage of the tree-based model, which can effectively extract cross features and provide interpretability according to inferred decision rules. Finally, extensive experiments on real-world bank branches datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of MATE, which outperforms baseline and state-of-art methods from 17% to 41%.
Motivation
This study focues on the development of a location prediction system. With such system, the president of the bank can not only pre-estimate the effectiveness of arbitrary locations to avoid building branches with poor performance but also help the bank branch become profitable in the near future.
The Proposed MATE
To summarize, the contributions of MATE are as follows:
- To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to propose a framework that combines tree-based models and neural networks to predict multi-performance for candidate bank branch locations. The MATE model can effectively extract complex cross features to represent regional characteristics and still maintains good interpretability of the model.
- We introduce a multi-task learning structure to predict the performance of six indicators, which are more in line with the bank’s actual needs. In addition, we propose a negative sampling strategy by using the FE module to solve the data imbalance problem. Therefore, our model can accurately and effectively predict the performance of every location in the city.
- Extensive experiments are conducted on real-world bank branches dataset, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed MATE model.
- Notably, MATE has been used for assisting the banker to deploy optimal branch locations in several cities in Taiwan in 2020.
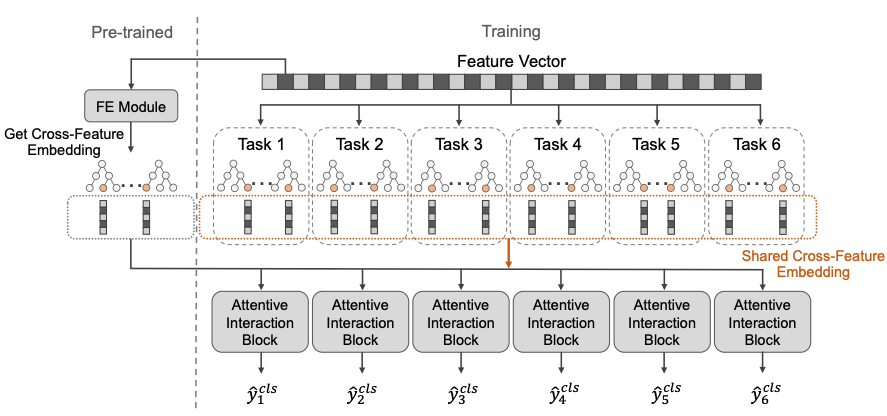
MATE Architecture.