Abstract
The Proposed INQSS
We propose the use of a magnitude spectrogram and scattering coefficients as inputs. To fuse two features, the input spectrogram and scattering coefficients, which are a concatenation of first- and second-order scattering coefficients, first pass through two separated CNNs and are then concatenated as the input of the BLSTMs. Although the scattering transform is considered to be similar to a CNN, we still process the scattering coefficients through CNNs to fine-tune the scattering coefficients. The outputs of the dense layers then provide the prediction results. In addition, we incorporate quality scores as the training targets to improve the performance of the intelligibility prediction. The quality prediction shares the same CNNs as the intelligibility prediction but uses a different BLSTM and dense layers. The details of the model structure are as follows:
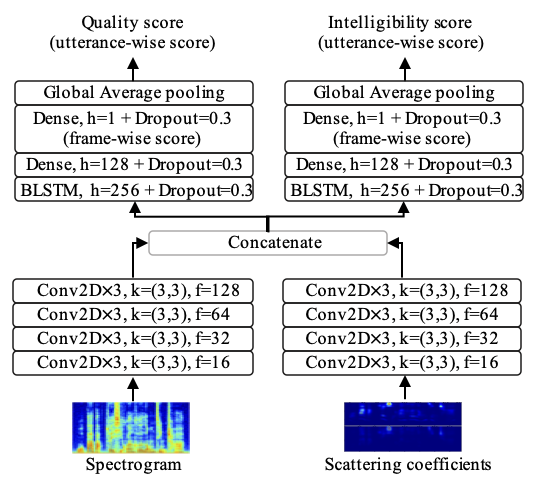
The TMHINT-QI Dataset
The TMHINT-QI dataset is a Chinese speech dataset with subjective quality scores and intelligibility scores. The speeches in TMHINT-QI include clean speech recorded in a quiet environment, artificially contaminated noisy speech, and enhanced noisy speech processed by the SE models. The goal of releasing TMHINT-QI is to promote research in speech quality assessment and intelligibility assessment models, which can be later used to evaluate the performance of speech processing and thus guide researchers to develop models that can generate results with better human perception.
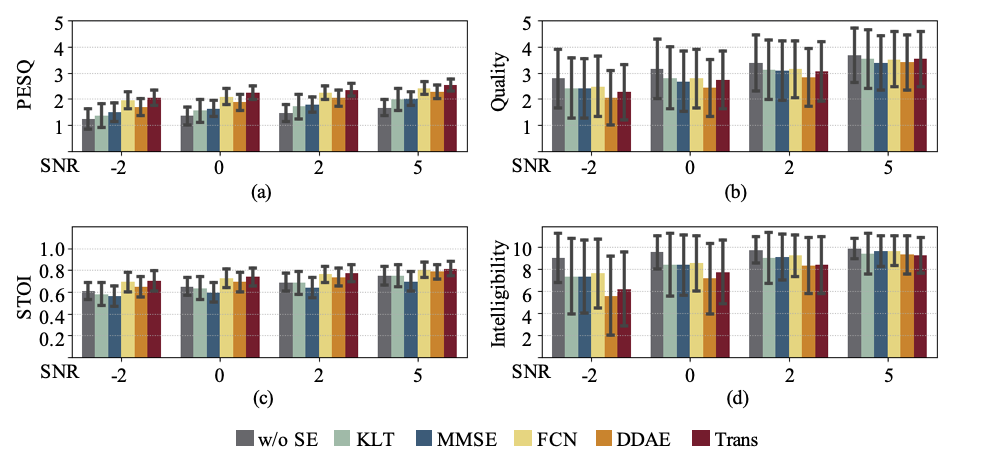
See Paper for more detail.